Brand Name: SGONEK
Price: $2400 -$3000/Kilogram
Place of Origin: Shaanxi, China
Certification: ISO FDA SG COA MSDS
Grade: Phamaceutical Grade
Payment Terms: T/T, Western Union, MoneyGram
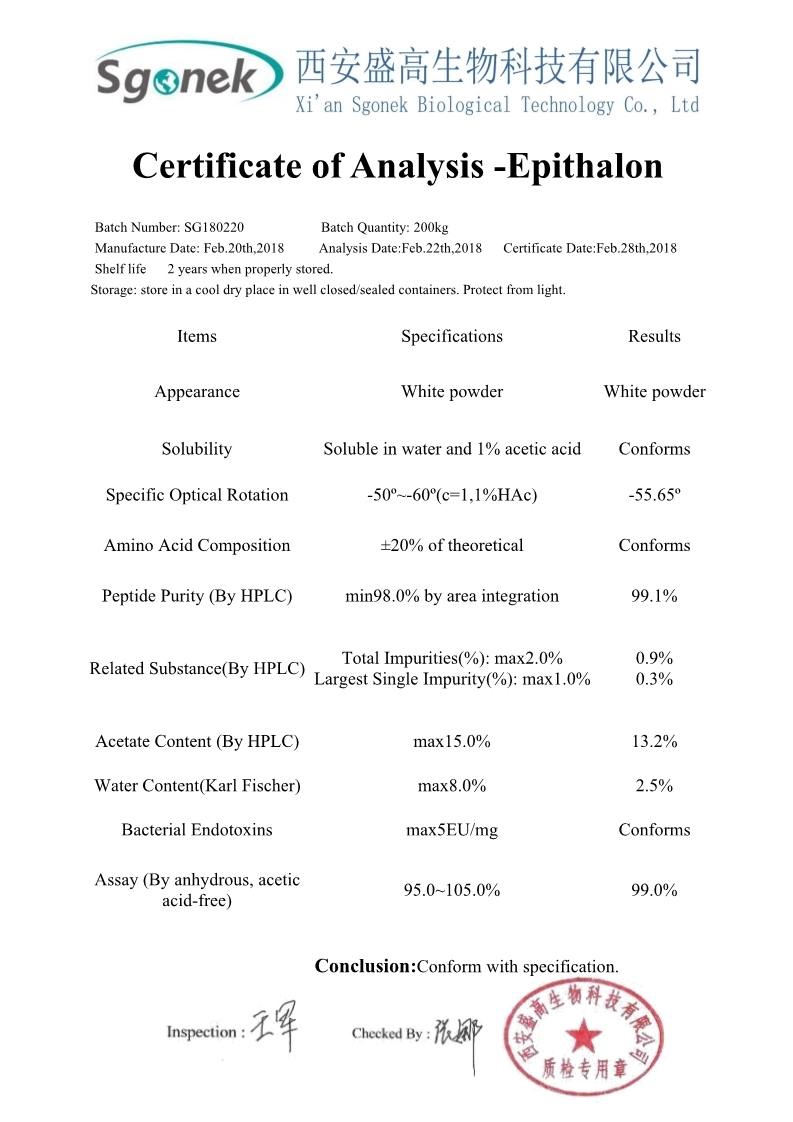
| Product Name: | Epithalon | Cas No.: | 307297-39-8 |
| Molecular Formula: | C14H22 N4 O9 | Purity: | 99%min |
| Brand Name: | SGONEK | Certification: | ISO FDA SG COA MSDS |

| Product Name: | Epitalon |
| Synonyms: | Epitalon;Epithalon;Glycine, L-alanyl-L-a-glutamyl-L-a-aspartyl-;L-alanyl-L-alpha-glutamyl-L-alpha-aspartylglycine;9: PN: WO02090380 PAGE: 55 claimed protein |
| CAS: | 307297-39-8 |
| MF: | C14H22N4O9 |
| MW: | 390 |
| Product Categories: |
Amino Acid Derivatives;Peptide
|
Epithalon is a peptide used to regulate the cell cycle through up-regulation of telomerase activity. The sequence of amino acids in the peptide is Alanine-Glutamate-Asparagine-Glycine. Animal studies have been done on the effects of Epithalon on suppression of spontaneous mammary tumors and spontaneous carcinogenesis. Studies have shown that the mode of action of Epithalon involves suppression of oncogene expression and modification of telomerase activity. A summary of the studies and research on telomerase is provided below.
An endocrine gland-pineal gland of an animal secreting a peptide called "Epithalamin", which can be synthesized by artificially synthesizing the tetrapeptide (Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly) called "Epithalon" The It has been reported that Epithalon has a certain tumor inhibitory effect in animals. The purpose of this study is to study the effect of Epithalon on the growth of HepG2 cells, the telomere length and the telomerase activity of HepG2 cells. At the same time, the effects of Epithalon on telomere and telomerase were studied by comparing the changes of telomere length and telomerase activity with Epithalonon human fetal hepatocyte L-02, and to explore its possible role mechanism.


Telomerase is a specific RNA (ribonucleic acid)-dependent polymerase that elongates and maintains the length of telomeres by adding tandem repeats on the chromosomal 3' end. The enzyme is composed of two parts: an RNA component which supplies the telomere template for elongation, and the catalytic subunit which possesses reverse transcriptase activity. These two parts work in tandem to avert telomere attrition especially in somatic cells. In vitro experiments have shown that telomere elongation promotes indefinite cellular proliferation and that suppression of telomerase activity promotes apoptosis of neoplastic cells. However, these studies have also shown that maintenance of telomere length within a range of 15-20 kilobase pairs does prevent tumorigenesis. All the research and studies done concerning telomerase do show that telomerase activity is limited to cell division through its action of stabilizing the telomere length.
Telomeres are located at either ends of a chromosome, and they do protect the adjacent gene sequence from shortening due to repeated replication cycles. Elongation of telomeres enables senescent cells to stabilize their telomeric length. However, excess elongation would enable such cells to exceed their Hayflick limit via evasion of apoptosis or the post-mitotic phase; and therefore, such cells have the potential of becoming immortal and this predisposes them to neoplastic transformation.
Human telomeres are made up of tandem repeats of the nucleotide sequence TTAGGG that form a T loop structure when associated with telomere-binding proteins. The T loop structure ensures the integrity of the telomeres by protecting them from constitutive degradation. These tandem repeats do shorten as a consequence of repeated chromosomal replication cycles. Such shortening is due to the inability of DNA polymerase to repeatedly replicate the nucleotides located in the T loop region. This leads to senescence or growth arrest, and a critically shortened telomere does induce a p53-mediated DNA checkpoint reaction. Some cells do evade senescence if they have nonfunctional p53 and/or pRb, but cell death still occurs due to either lethal DNA rearrangements or chromosomal fusion. Thus, evasion of telomere-mediated senescence is the main way that cells use to avert premature senescence and apoptosis. This occurs only when telomerase activity is up-regulated. Telomerase elongation leads to stabilization of the genotype as the rate of gene mutation is maintained within normal limits. However, an increase in the rate of apoptosis leads to a proportionate increase in cellular regeneration rate, and this causes an increase in the number of sporadic gene mutations that occur thus predisposing the person to pro-neoplastic mutations.
Current studies show that telomere shortening is associated with chronic diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis, coronary artery disease, diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer’s disease, though their findings are still considered inconclusive. Based on the findings of these studies, it can be theorized that Epithalon could prevent the development of these diseases.